Google for Jobs has long been eagerly awaited in the German-speaking HR scene. The service has been active in Germany since March 2019, followed by the launch in Switzerland in September 2019. Only job seekers in Austria still have to do without it (as of September 2020). This raises a few questions for recruiters: Will Google for Jobs really revolutionize the recruiting market? What are the benefits of the service for recruiters and job seekers? And how do companies manage to optimally place their job advertisements in the Google for Jobs Box and thus take their e-recruiting to a new level?
How does Google for Jobs work?
Google for Jobs is a feature of Google and not a job platform in the traditional sense. Job listings are displayed on Google's first page of search results in a special info box. To do this, Google collects information about job postings from all websites that are in the search index. For each search phrase, the most relevant hits are displayed with a source in the result box. The search queries can be more general or very specific ("Jobs in Munich" vs. "Job industrial mechanic Munich part-time").
Since Google for Jobs is not a job platform, postings cannot be uploaded directly. Instead, the search engine recognizes which web pages are job postings and displays them if they match the search query.
The decisive factor here is the "structured data". This is information in the HTML code of a website. They don't just let the search engine know that the content of a page is a job posting. Further information is also provided here in a fixed format. For example, the exact job title, the place of work and details of the possible salary.
Optimize job ads for Google for Jobs
The job advertisement box appears on Google on the first page of search results above the "normal" organic hits. In addition, it is visually highlighted. Due to this prominent placement, it is something like free advertising for recruiters: Advertisements that end up here reach significantly more potential applicants. However, other companies also want to claim this free advertising for themselves.
Provide the information you need in the right format
Job postings must therefore be optimized for Google's job box. First of all, this only means that they have to be indexable and readable by the search engines. As already mentioned, Google obtains the information for the job box from the structured data of websites. In order for online job advertisements to be listed, this data must be prepared in accordance with Schema.org's specifications.
Schema.org is an open community founded by Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex. To put it simply, their goal is to create a common vocabulary with which structured data is made available to search engines. This data is inserted into the head section of the website. Google recommends using the JSON-LD format for this.
For job advertisement websites, the following information is required or at least recommended:
- "title" (the title of the tender)
- "industry"
- "datePosted" (the publication date)
- "description" (the description of the job advertisement)
- "validThrough" (the expiration date of the job advertisement)
- "employmentType" (the scope of employment, e.g. "[FULL_Time]" = full-time)
- "jobLocation" (the address of the place of work)
- "jobLocationType" (the type of work location; e.g. "[TELECOMMUTE]" can also be entered here if the work is done from home)
- "hiringOrganization" (the name of the hiring organization)
- "jobStartDate" (the date from which the position is vacant)
- "workHours" (the typical working hours)
- "baseSalary" (the expected base salary)
Basically, you can assume that the more information Google receives about a job advertisement, the more likely it is to end up in the job box. Information such as the "baseSalary" is not mandatory. However, it is believed that Google will prefer job postings that contain this important information for job seekers.
When posting jobs on your own career page, make sure that the required data is entered in the correct format!
Tip: Highlight home office positions in a targeted manner
Due to COVID-19, many companies are allowing their employees to work from home. Not only does this significantly reduce the risk of infection – it also makes your company attractive to talent. Google's search trends show that interest in ways to work from home skyrocketed in March and April 2020. Even today, it is still significantly higher than before the Corona pandemic.
Google for Jobs takes this into account by allowing job seekers to filter for specific job opportunities in the home office. In order for a job posting to appear among these search results, it must contain the appropriate meta information. This is done using the jobLocationType: "TELECOMMUTE" markup. For more information, see Google's overview of structured data.
In the U.S., job postings marked accordingly are highlighted in search results with a "home office" flag. It can be assumed that this feature will soon be available in Germany and Switzerland as well.
Infographic: How Google for Jobs Is Changing Recruiting
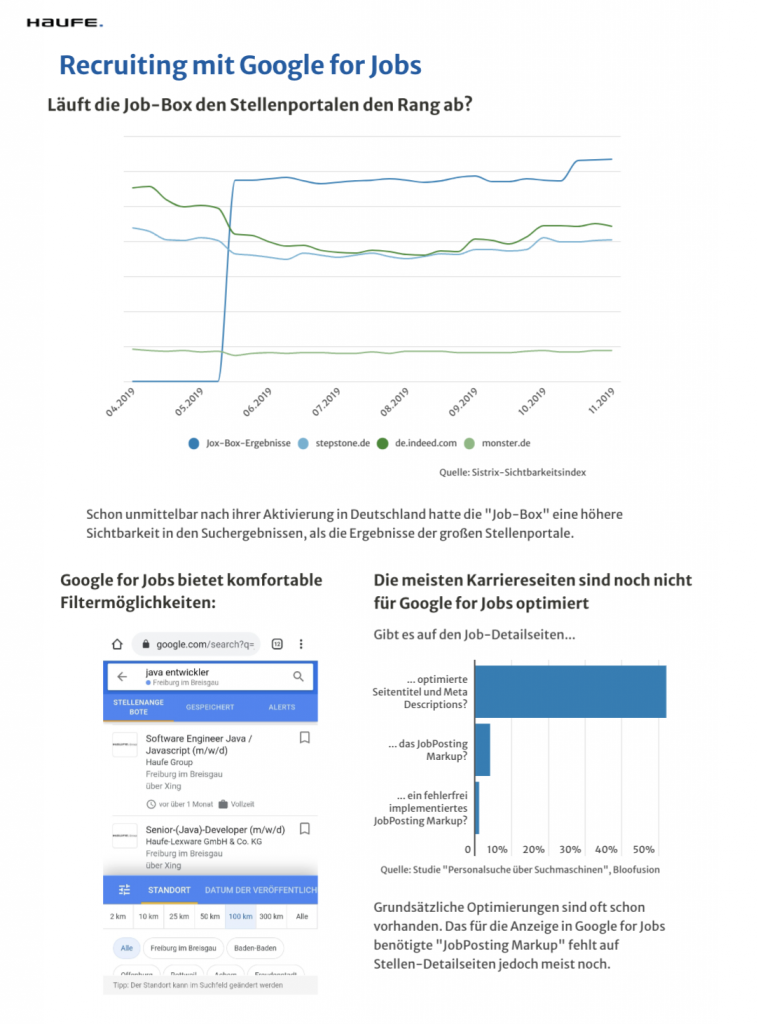
Advertisements on job boards
Most companies publish job advertisements not only on their careers page, but also on the relevant job portals. Some of them already capture the data in the appropriate format so that it can also be displayed in the Google for Jobs Box. This includes listings on XING, Stellenanzeigen.de, Monster, Facebook Jobs, LinkedIn and Glassdoor.
Job advertisements from the two major providers Indeed and StepStone are currently (as of November 2019) not displayed in the Google for Jobs box.
The easier way to the job box: Using recruiting software
Suitable Applicant Management systems automatically record the relevant data in such a way that search engines can work with it. This increases the likelihood that a job advertisement will appear in a prominent position on Google. For recruiters, this means that more potential applicants become aware of them. And all without any knowledge of HTML!
However, the following recommendation also applies when using Applicant Management software: Provide potential applicants with as much information as possible. Google only displays the job advertisements in the job box that the algorithm considers to be the most helpful for applicants. Transparency helps here. Companies should therefore consider including information on salary, working hours, flexitime arrangements, etc. in their job advertisements.

Christoph Herzog
Editor: Haufe Talent
Christoph Herzog is interested in people and how they can work better together in the digital age. He is an editor at the Haufe Group, father of a daughter and likes to walk on narrow paths.




